Dynamic Graphic Design Definition: The Complete Expert Guide (2025 Edition)
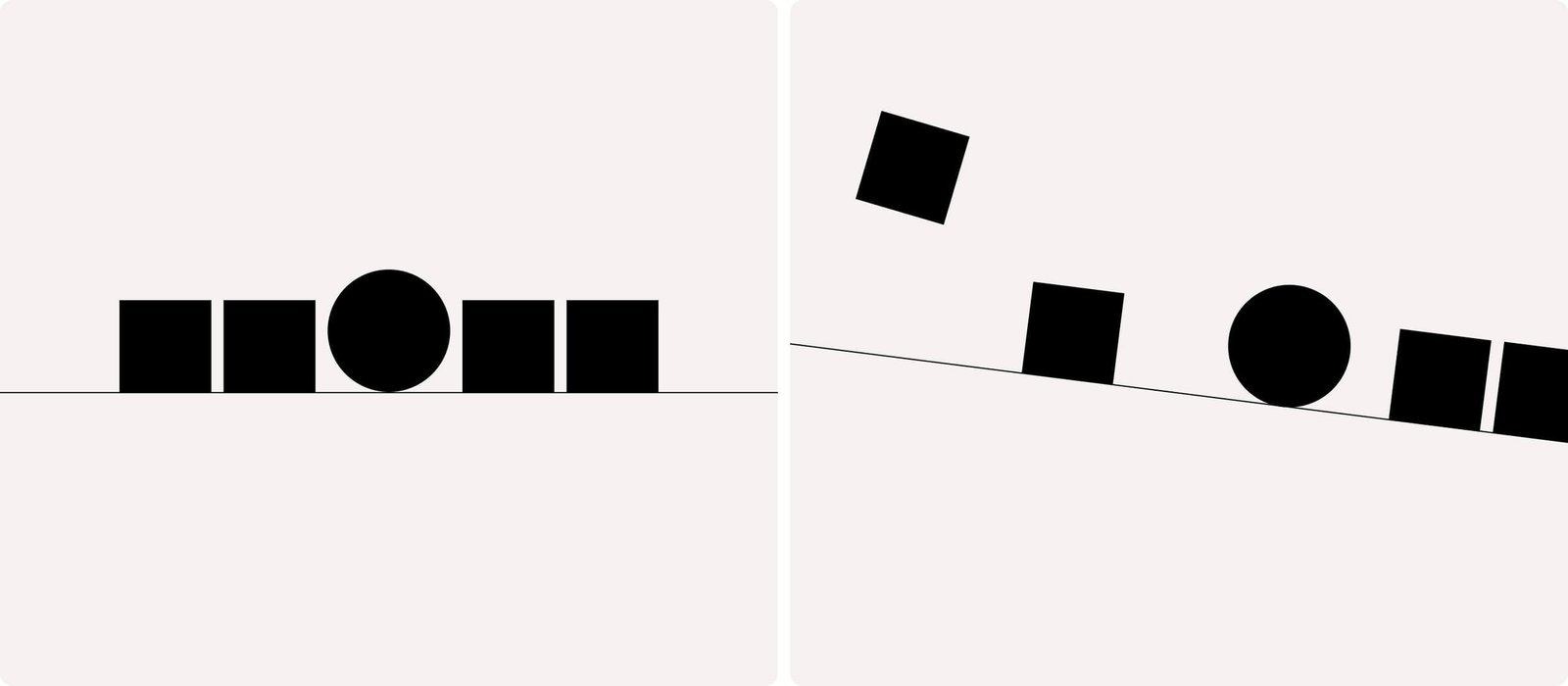
Dynamic graphic design refers to a visual communication approach where design elements adapt, move, or evolve based on time, interaction, or data. Unlike static graphics, dynamic designs respond to context, creating living visuals that react to environment, platform, or audience behavior.
In professional terminology, dynamic design integrates motion, algorithmic logic, and responsiveness into the visual structure bridging graphic design, motion design, and interactive media.
This guide provides the most comprehensive definition of dynamic graphic design, detailing its evolution, features, applications, and influence across branding, UX, and digital communication.
1. Dynamic Graphic Design Definition
Dynamic graphic design is the discipline of crafting visual systems that change over time or interaction while maintaining coherent identity.
It merges design principles (color, form, typography) with temporal behavior (motion, transformation, responsiveness).
Core Definition (Authoritative Version)
Dynamic graphic design is the creation of visual compositions whose form, layout, or motion evolve in response to contextual inputs such as time, user behavior, platform, or environmental data — while preserving the designer’s intended identity system.
This means every visual component — typography, color, shape, or animation — can shift dynamically within defined constraints, ensuring adaptability and interactivity without losing brand coherence.
2. Evolution of Dynamic Design: From Static Layouts to Living Systems
| Era | Design Type | Defining Feature | Tools / Technologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950s–1980s | Static Print Design | Fixed layout, analog reproduction | Lithography, Offset Printing |
| 1990s | Digital Graphic Design | Digital manipulation, raster/vector tools | Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator |
| 2000s | Motion Graphics | Time-based visuals, broadcast media | After Effects, Flash |
| 2010s | Responsive & Interactive Design | Layout adaptation and web animation | CSS3, HTML5, JavaScript |
| 2020s | Dynamic Design Systems | Real-time, data-driven visual behavior | AI, Generative Algorithms, WebGL |
The current era (2020–2025) defines dynamic design not merely by motion, but by systemic adaptability — designs that live, react, and evolve.
3. Core Components of Dynamic Graphic Design
Dynamic design operates through interrelated components that manage variability and coherence.
3.1 Dynamic Elements
-
Motion – Animation or transitions that express time-based change.
-
Interaction – Visual responses triggered by user input.
-
Data Adaptation – Visuals that modify according to real-time data or environment.
-
Responsive Layout – Designs that auto-adjust to screen or platform.
-
Generative Structure – Algorithmic rules that create infinite variations.
3.2 Constant Elements
-
Brand Identity Core – Symbolic or structural constants (e.g., logo skeleton).
-
Color Philosophy – A unified palette ensuring visual harmony.
-
Typography System – Consistent typographic ratios and weights.
-
Grid and Composition Logic – Underlying structure that anchors movement.
Dynamic design succeeds only when variation aligns with identity.4. Characteristics of a Dynamic Graphic Design System
| Attribute | Description | Practical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptable | Responds to device, environment, or user | Seamless cross-platform experience |
| Responsive | Adjusts proportionally without distortion | Improved readability & engagement |
| Interactive | Invites user participation | Higher dwell time |
| Animated | Utilizes time-based motion for storytelling | Emotional and visual depth |
| Contextual | Changes depending on data or event | Real-time relevance |
| Consistent | Retains core identity values | Brand recognizability |
5. Types of Dynamic Graphic Design
5.1 Animated Visuals
Animation breathes life into static elements. Logos can spin, shapes morph, and typography move to guide the viewer’s eye.
Example: Animated explainer videos or social media posts using kinetic typography.
5.2 Interactive Interfaces
Dynamic web design integrates graphics that react to user input—clicks, scrolls, or gestures.
Example: Interactive landing pages where visuals adapt to mouse movement.
5.3 Generative Branding
Design systems powered by algorithms or data streams produce endless variations of a visual identity.
Example: AI-generated campaign visuals changing color based on weather or location.
5.4 Responsive Layouts
Design frameworks adapt automatically to devices or screens without loss of proportion or clarity.
Example: Websites whose composition changes seamlessly from desktop to mobile.
5.5 Motion-Integrated Infographics
Dynamic infographics use animated sequences to visualize changing data.
Example: Data dashboards or animated statistical visuals in presentations.
6. Principles Behind Dynamic Design
-
Consistency in Change – Variation occurs within a structured rule set.
-
Timing and Rhythm – Smooth pacing of motion maintains visual flow.
-
Hierarchy and Focus – Animation supports, not distracts from, message hierarchy.
-
Simplicity in Complexity – Limit transitions to meaningful motion only.
-
Feedback Awareness – Interactive motion responds immediately to user action.
-
Performance Balance – Maintain optimal loading and frame rates for smooth operation.
These principles ensure motion remains purposeful rather than decorative.
7. Importance of Dynamic Graphic Design in Digital Media
Dynamic design strengthens communication across fast-changing digital environments.
-
Brand Flexibility: Logos adapt to different moods, platforms, or campaigns.
-
User Retention: Motion increases engagement metrics and dwell time.
-
Information Clarity: Animated transitions guide users through complex data.
-
Modern Aesthetic: Reflects technological fluency and forward-thinking identity.
-
Cross-Media Continuity: Consistent motion language unites print, web, and video materials.
Companies like Spotify, Google, and Airbnb employ dynamic systems to create adaptable brand ecosystems.
8. Dynamic Design vs. Static Design
| Criteria | Static Design | Dynamic Design |
|---|---|---|
| Movement | None | Uses motion & transformation |
| Adaptation | Fixed layout | Context-responsive |
| Engagement | Passive viewing | Interactive participation |
| Relevance | Time-bound | Real-time contextual |
| Production | One-time creation | Continuous evolution |
| Brand Identity | Immutable | Evolving but consistent |
Dynamic design surpasses static design by making branding alive, not frozen.
9. Applications of Dynamic Graphic Design
9.1 Branding & Visual Identity
Modern brands use dynamic logos and color systems that adjust according to data or context.
Example:
-
A logo that changes hue based on season or event.
-
Social media banners with adaptive shapes for campaigns.
9.2 User Interface (UI) and UX Design
Dynamic transitions enhance usability, showing users where actions lead.
Example: Button hover animations, loading transitions, and gesture feedback.
9.3 Advertising & Marketing
Animated banners and personalized visual content create emotional resonance and better recall.
Example: Real-time ads that change visuals based on user demographics.
9.4 Motion Design & Video Production
Dynamic typography, layered animation, and visual storytelling in film titles or reels.
9.5 Data Visualization
Animated infographics and dashboards display evolving metrics, making trends understandable.
10. Tools and Technologies for Dynamic Graphic Design
| Category | Tools / Frameworks | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Motion Graphics | Adobe After Effects, Blender | Keyframe animation, compositing |
| Web Animation | CSS3, GSAP, Lottie, WebGL | Interactive animations |
| Generative Design | Processing, p5.js, TouchDesigner | Algorithmic creation |
| 3D Motion | Cinema4D, Unreal Engine | 3D dynamics & motion |
| Branding Systems | Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD | Responsive and dynamic prototyping |
Emerging tools integrate AI-driven automation, producing adaptive motion sequences without manual keyframes.
11. Process of Creating a Dynamic Graphic Design
Step 1 – Define Core Identity
Establish the non-variable foundation: brand voice, logo geometry, and base colors.
Step 2 – Select Dynamic Parameters
Choose what changes — motion pattern, data input, or layout adjustment.
Step 3 – Design Motion Language
Create consistent animation rules: direction, easing, duration, and rhythm.
Step 4 – Prototype and Test
Use motion prototypes to assess fluidity and user perception.
Step 5 – Implement Across Media
Integrate the system into digital assets, ensuring smooth adaptation.
Step 6 – Monitor and Update
Analyze interaction metrics and refine behaviors for performance and consistency.
12. Advantages and Limitations
12.1 Advantages
-
Enhances brand recall through engaging movement.
-
Encourages interaction and participation.
-
Delivers contextual relevance.
-
Supports cross-platform coherence.
-
Improves information delivery speed.
12.2 Limitations
-
Requires higher technical skillset.
-
May increase production cost.
-
Needs compatibility testing across devices.
-
Poorly executed motion can cause visual fatigue.
13. Dynamic Graphic Design in Branding Strategy
Dynamic branding redefines identity as fluid yet recognizable. Instead of one logo, a brand possesses a system of identities derived from a single genetic visual code.
Key Components of a Dynamic Brand:
-
Core logo grid or DNA
-
Rule-based transformations
-
Modular patterns and data-driven variants
-
Real-time contextual output
This approach ensures visual freshness while maintaining recognizable DNA.
14. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Dynamic Design
AI transforms dynamic design through automation and prediction:
-
Machine learning algorithms generate unique layouts per user.
-
Predictive animation optimizes motion paths for engagement.
-
Neural style transfer adapts design aesthetics instantly.
-
Real-time content generation creates infinite contextual variants.
AI allows designers to shift from manual animation to system orchestration.
15. Future of Dynamic Graphic Design (2025–2030 Outlook)
-
Hyper-Personalized Visuals: Designs adapt based on individual data.
-
Voice-Triggered Interfaces: Dynamic graphics respond to vocal cues.
-
3D & Spatial Motion: AR and VR will integrate dynamic branding in real environments.
-
Zero-Code Motion Platforms: AI tools generate responsive animation automatically.
-
Ethical Motion Standards: Industry guidelines will define accessibility in motion design.
16. Key Takeaways
-
Dynamic graphic design = visual adaptability + contextual intelligence.
-
It connects design systems, data, and interactivity under one visual logic.
-
Motion is not decoration; it’s a communicative layer that informs meaning.
-
Successful dynamic systems maintain variation with consistency.
-
The future belongs to real-time, data-responsive, and AI-assisted visual systems.
17. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the core definition of dynamic graphic design?
Dynamic graphic design is the creation of adaptable, motion-based, or context-aware visuals that change over time while maintaining consistent identity rules.
Q2. How does dynamic design differ from static design?
Static design remains fixed, while dynamic design evolves with interaction, device, or data, offering responsiveness and engagement.
Q3. Which industries use dynamic graphic design the most?
Technology, entertainment, marketing, fintech, and e-learning sectors adopt dynamic visuals for brand interactivity and adaptive storytelling.
Q4. What are the best tools for dynamic graphic design?
Adobe After Effects, Figma, Lottie, GSAP, and Processing are the most effective tools for motion, interaction, and generative visuals.
Q5. Can dynamic design improve SEO and digital visibility?
Yes. Motion-rich and interactive visuals increase user engagement, dwell time, and shareability—key behavioral metrics that enhance SEO performance.
Q6. Does dynamic design affect loading speed?
When optimized with vector-based or lightweight animation (SVG, JSON), it maintains performance without significant load impact.
Q7. How does AI influence dynamic design?
AI automates animation creation, contextual adaptation, and predictive behavior, enabling large-scale personalization in branding and UX.
Q8. What makes a dynamic design successful?
Consistency of core identity, meaningful motion, contextual adaptability, and smooth performance across all devices.
Learn More: What Is the Opposite Color of Brown? Complete Guide
What Color Represents Peace? Symbolism, Culture, and Global Meaning
Conclusion
Dynamic graphic design redefines visual communication as a living process.
It is not motion for aesthetic pleasure, but a systematic adaptation of identity that mirrors how brands and users interact in a digital-first ecosystem.